Equine Diagnostic Imaging
Our staff is proud to offer a wide variety of equine veterinary services, utilizing minimally invasive surgical technologies for high-performance horses and equine athletes. Our team of dedicated staff have the experience and expertise, as both veterinarians and horsemen, to treat any equine condition in racing breeds and sport horses, breeding stock, Western disciplines, and more.
Give Your Horse the Winning Edge
Our expert team is dedicated to providing comprehensive diagnostics, treatments, and rehabilitation tailored to your horse's needs.
Computer Tomography (CT)
Computed Tomography (CT) has become an important tool in diagnostic medical imaging since the 1970’s. More recently CT has been used for preventative medicine and screening for a variety of diseases in humans. In Veterinary Medicine, CT is commonly used to image the head & brain, lungs, spine, abdominal & pelvic areas, and extremities. Additionally, contrast can be used in a variety of imaging studies as well.
CT imaging is very important tool in diagnosing and planning fracture repair in horses because of the multiplanar reconstruction views and the 3 dimensional reconstruction capabilities.
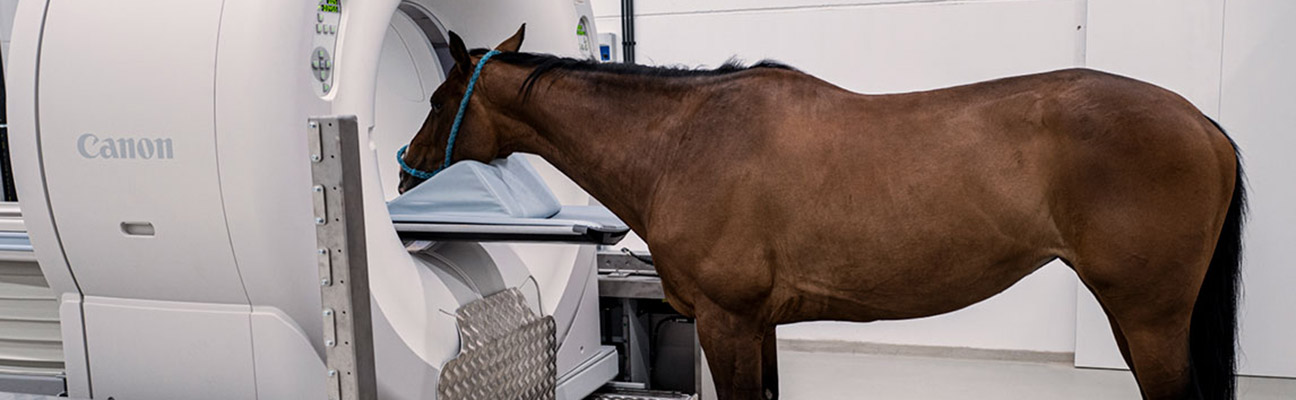
We are excited to announce that Caesars Entertainment Equine Specialty Hospital is one of the first in the U.S. offering groundbreaking diagnostic capability with the newly installed Qalibra Computed Tomography (CT) system. Designed specifically for equine patients, the unique system features the world’s largest field-of-view and is height adjustable to match the size of the horse, making it possible to scan patients while they are safely standing or under general anesthesia or light sedation.
What can be scanned with our robotic CT?
- Equine Head
- Bone in general, especially when radiographs are non-diagnostic
- Dental disease (e.g. specific diagnosing diseased tooth for extraction)
- Nasal passages, sinuses, orbit
- Brain
- Cervical spine (proximal)
- Hyoid apparatus (THO & TMJ)
- Tumors
- Equine distal limb (including the carpus & tarsus)
- Bone in general, especially when radiographs are non-diagnostic
- Stress fractures, non-displaced fractures (hair line fractures)
- Multiple forms of Osteochondrosis
- Navicular Bone Disease Syndrome
- Osteoarthritis
- Fracture diagnosis & repair planning (MPR and 3D Recon)
- Fracture healing comparison without general anesthesia
- Chronic Laminitis
Digital Radiography
Caesars Entertainment Equine Specialty Hospital utilizes a portable digital x-ray unit, which allow computerized enhancement of detail in specific regions of interest. Digital radiology units provide high quality images of limbs and the cervical spine. The images are immediately available for sit down review between the doctor and clients.
Diagnostic Ultrasound
Ultrasonography is a specialized imaging technique used to examine soft tissues and bone surfaces. This procedure uses a hand held device, called a transducer, to send and receive high frequency sound waves. As the sound waves move into tissue, they are reflected back and transformed into an image that can be seen on a video screen. It is one of our most frequently used diagnostic tools and is used to diagnose conditions such as tendon, ligament and joint injuries, pleural pneumonia, umbilical infections, colic and abdominal disease, cardiac disease, ocular issues and any swelling or mass, in addition to evaluating late term pregnancy. Ultrasound is commonly utilized for guided biopsies of the kidney, liver, lung, or masses. We also utilize this modality for ultrasound guided injections into bursas, tendons/ligaments, the sacroiliac space, and cervical facets.
Endoscopy
An endoscope is a small flexible fiber optic tube with a videocamera that allows direct visualization of internal structures. The endoscope allows examination and evaluation of otherwise inaccessible structures such as the upper respiratory tract (including the pharynx, trachea and guttural pouches), the upper gastrointestinal tract, the ears (otoscopy), the urethra and bladder as well as the cervix and uterus in the mare. Videoendoscopy allows the image to be displayed on a monitor, in addition to providing video imaging capabilities for clients & referring veterinarians.
Dynamic Endoscopy
Dynamic endoscopy is a method of analyzing upper airway problems during exercise. The Dynamic Endoscope is lightweight and halter-mounted as opposed to a static tower-mounted scope. The Endoscope is placed into the horse’s nasal cavity visualizing the larynx. This placement gives an excellent view of the larynx function during workouts. The horse can be either be lunged or ridden to exacerbate signs of problems not otherwise visible with standard static endoscopy exams.
The benefits of Dynamic endoscopy are that we can potentially diagnose upper airway problems during workouts where they are more likely to occur using your standard equipment and in the horse’s natural workout environment. The system is rider independent and it can be reviewed immediately after exercise. It can be reviewed in slow motion for better assessment of the airway function and emailed to your referring veterinarian for a completeness and follow-up.
Nuclear Scintigraphy
Commonly known as a bone scan, nuclear scintigraphy is an imaging technique allowing changes in metabolic activity of soft tissue or bone to be visualized. It is one of the most commonly performed nuclear medicine procedures and is particularly useful in detecting bone inflammation in difficult to diagnose lameness cases. It is also valuable for patients with stress fractures, where a dynamic lameness exam is contraindicated. This procedure is highly sensitive for detecting early disease, allowing evaluation of the entire skeleton or a specific region, and the procedure is done without anesthesia.
A small amount of radioisotope pharmaceuticals are injected into the jugular vein through a catheter. These drugs become concentrated where bone is actively remodeling or undergoing change and identifies the suspected areas of injury. These “hot spots” are then imaged with radiographs and/or ultrasound for further evaluation.
If you would like more information on this procedure, please contact us via email at CESH@purdue.edu or call us at 317-398-1980 and we will be happy to assist you.

